Dementia, anxiety, and depression are three conditions that can be challenging to deal with on their own. But what if you’re dealing with two or even all three at once? This is a common scenario for many people, especially older adults. The connections between these three conditions are complex and multifaceted, and understanding them can help you better cope with their impact on your life.
What is Dementia?

Dementia is a general term that describes a decline in cognitive function severe enough to interfere with daily life. This decline is often characterized by memory loss, difficulty with language, problems with visual-spatial orientation, and changes in mood and behavior. Dementia is not a specific disease but rather a group of symptoms that can be caused by various conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and vascular dementia.
What is Anxiety?
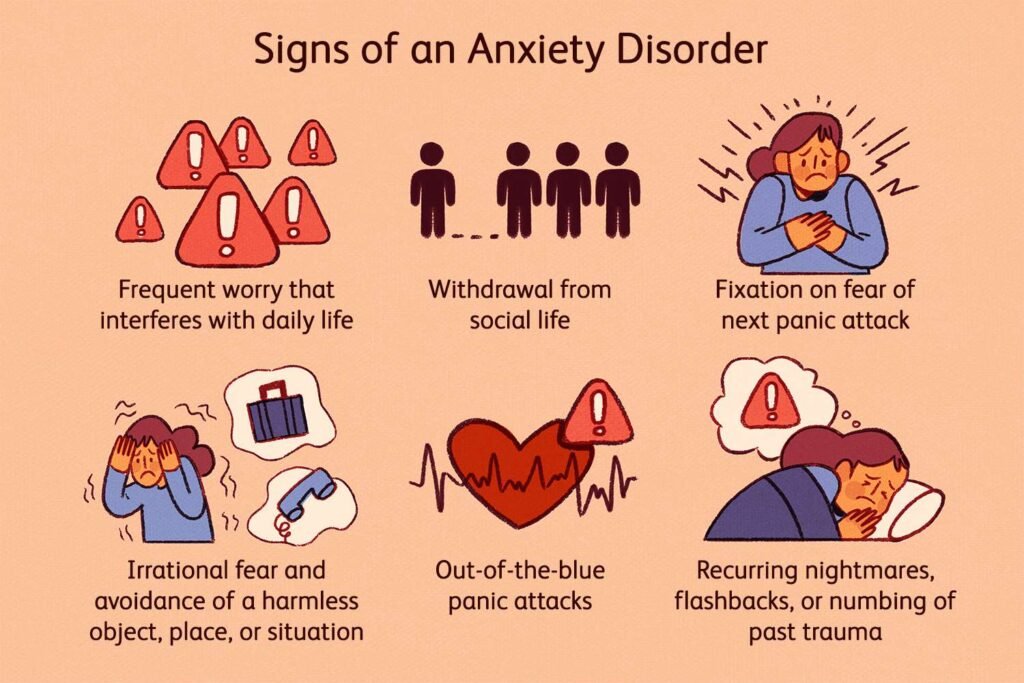
Anxiety is a normal and sometimes helpful response to stress or danger. It can help us stay alert and focused, motivate us to take action, and protect us from harm. However, when anxiety becomes excessive or irrational, it can interfere with our daily activities and cause significant distress. Symptoms of anxiety can include excessive worry, restlessness, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and physical symptoms such as sweating, shaking, and palpitations.
What is Depression?

Depression is a mood disorder that can cause persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest in life. It can also lead to physical symptoms such as fatigue, changes in appetite and sleep, and aches and pains. Depression can be caused by various factors, including biological, genetic, environmental, and psychological factors.
Connections between Dementia, Anxiety, and Depression
While dementia, anxiety, and depression are distinct conditions, they are often interconnected. For example:
- People with dementia are at an increased risk of developing anxiety and depression. This may be due to the stress of coping with cognitive decline, the emotional impact of losing independence, and changes in social relationships.
- Anxiety and depression can also increase the risk of developing dementia. Chronic stress and inflammation have been linked to brain changes that can contribute to dementia. Additionally, untreated depression can lead to cognitive impairment.
- Some of the symptoms of dementia, such as memory loss and confusion, can be mistaken for anxiety or depression. This can lead to misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis of dementia.
Finally, some of the medications used to treat anxiety and depression can worsen cognitive function, which can exacerbate dementia symptoms.
Coping Strategies
Given these connections between dementia, anxiety, and depression, it’s important to take a comprehensive approach to managing these conditions. Here are some coping strategies that can help:
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle. Eating a balanced diet, staying physically active, getting enough sleep, and reducing stress can all help to manage symptoms of dementia, anxiety, and depression.
- Seek social support. Staying connected with friends and family members can help to reduce feelings of isolation and improve overall well-being.
- Manage symptoms with medication. Medications can be helpful in managing symptoms of anxiety and depression, but it’s important to work closely with a healthcare provider to find the right medication and dosage.
- Participate in therapy. Talking with a mental health professional can provide valuable support and guidance for managing anxiety and depression. Additionally, some types of therapy, such as cognitive behavioral therapy, can be effective in managing symptoms of dementia.
Can anxiety lead to dementia?
There is evidence to suggest that anxiety may increase the risk of developing dementia later in life. While anxiety is a normal response to stress and danger, chronic and severe anxiety can lead to changes in the brain that may contribute to the development of dementia.
One study published in the BMJ found that people with a history of severe anxiety had a higher risk of developing dementia than those without a history of anxiety. The study followed over 3,000 people for 10 years and found that those who reported high levels of anxiety at the beginning of the study had a 48% higher risk of developing dementia compared to those with low levels of anxiety.
Can depression and anxiety lead to dementia
Research suggests that depression and anxiety may be associated with an increased risk of developing dementia later in life, although the exact relationship is still unclear and requires further investigation.
Depression has been found to be a risk factor for developing dementia, particularly in late-life depression. A study published in the journal JAMA Psychiatry found that older adults with a history of depression had a higher risk of developing dementia compared to those without a history of depression. The study followed over 10,000 people for 28 years and found that those with a history of depression were 50% more likely to develop dementia.
Anxiety has also been linked to an increased risk of developing dementia. A study published in the BMJ found that people with a history of severe anxiety had a higher risk of developing dementia than those without a history of anxiety. The study followed over 3,000 people for 10 years and found that those who reported high levels of anxiety at the beginning of the study had a 48% higher risk of developing dementia compared to those with low levels of anxiety.
While the exact mechanisms underlying the relationship between depression, anxiety, and dementia are not yet fully understood, it is thought that these conditions may contribute to changes in the brain that increase the risk of developing dementia. For example, depression and anxiety may lead to inflammation and stress, which have been implicated in the development of dementia.
It is important to note that not everyone who experiences depression or anxiety will go on to develop dementia. However, managing these conditions through appropriate treatment, such as therapy and medication, may be important for overall brain health and reducing the risk of dementia.

Ayurvedic treatments that may be helpful for dementia, anxiety, and depression:
Meditation: Ayurveda places a strong emphasis on mental and emotional balance, and meditation is one of the most effective tools for achieving this. Regular meditation can help reduce anxiety and depression, and may also improve cognitive function in people with dementia.
Ayurvedic herbs: Ayurvedic herbs such as ashwagandha, brahmi, and shankhapushpi are known for their ability to promote mental clarity, reduce anxiety and depression, and support cognitive function. These herbs can be taken in the form of supplements or as part of an herbal formula prescribed by an Ayurvedic practitioner.
Ayurvedic massage: Ayurvedic massage, or abhyanga, is a form of massage that uses warm herbal oils to help relax the body and mind. This can be especially helpful for reducing stress and anxiety.
Diet and lifestyle changes: Ayurveda emphasizes the importance of a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle habits for maintaining good health. Making changes such as reducing caffeine intake, getting regular exercise, and eating a balanced diet can all be helpful for reducing symptoms of anxiety, depression, and dementia.
Panchakarma: Panchakarma is an Ayurvedic detoxification and rejuvenation therapy that involves a series of treatments to cleanse the body and balance the doshas (energies). Panchakarma can be helpful for reducing stress, anxiety, and depression, and may also improve cognitive function in people with dementia.
Patients can schedule an appointment with a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner at Vaidban Ayurved Bhawan by calling +91 8283060000 or sending an email to info@vaidban.com.