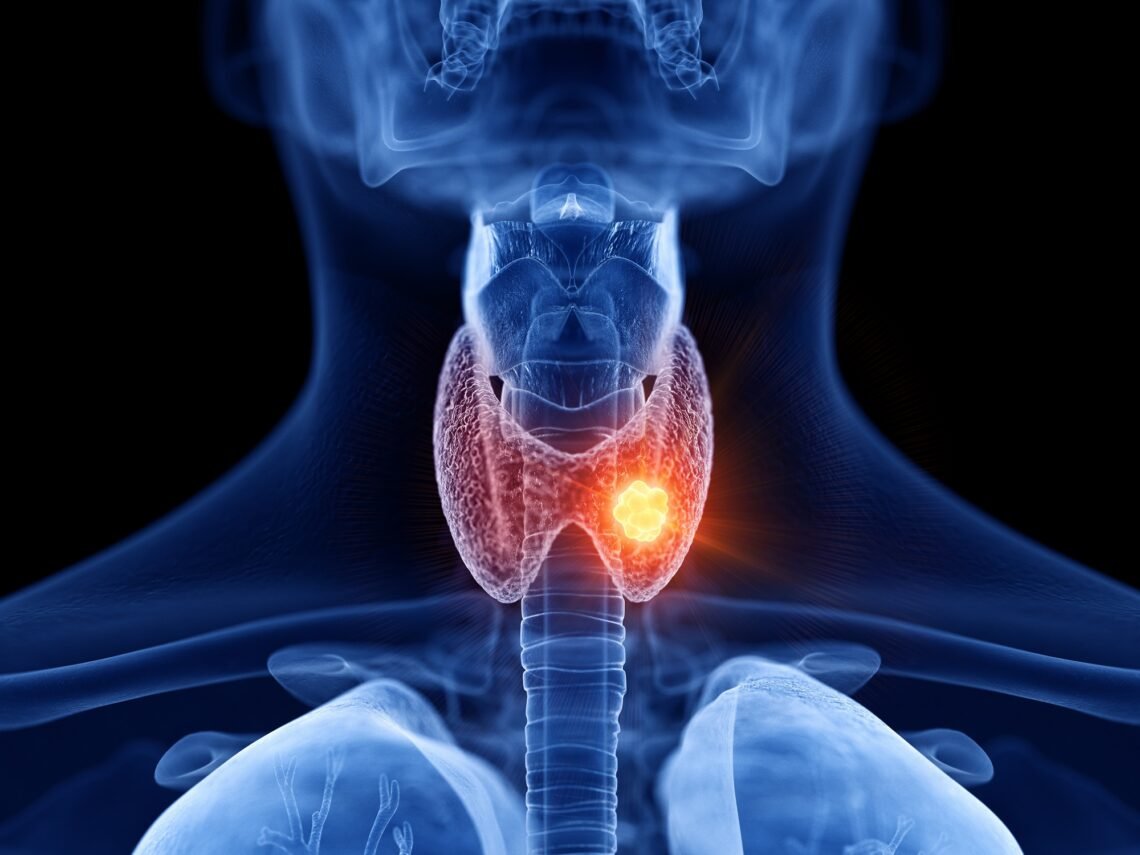
Thyroid disease affects millions of individuals globally. The thyroid, a small, butterfly-shaped gland in the front of the neck, is vital for regulating metabolism and energy levels. This blog will explore what thyroid disease is, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, helping you understand and manage it effectively.
What is Thyroid Disease?
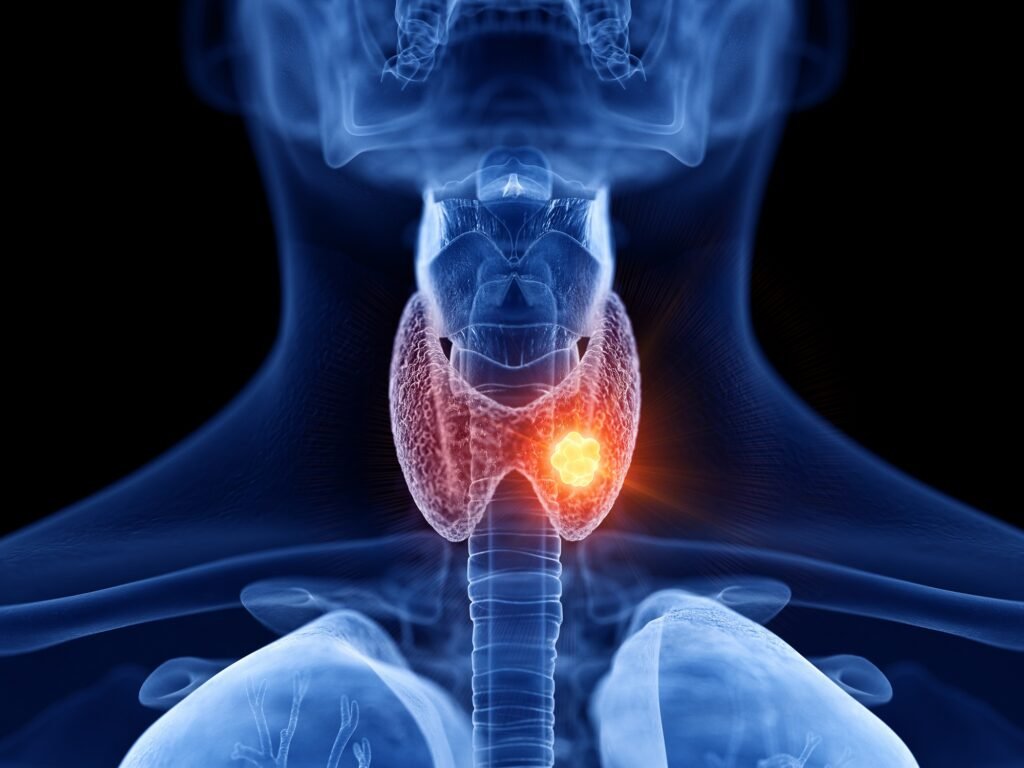
Thyroid disease refers to any condition affecting the thyroid gland, leading to an imbalance in hormone production. The two main types are hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.
- Hypothyroidism: This condition occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone, leading to symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, and depression. It can be caused by autoimmune disorders like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or iodine deficiency.
- Hyperthyroidism: This occurs when the thyroid gland produces too much hormone, causing symptoms like weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and anxiety. Graves’ disease, an autoimmune disorder, is a common cause.
- Other Conditions: These include thyroid nodules, goiter, and thyroid cancer. Nodules are lumps that can form in the thyroid, a goiter is an enlarged thyroid, and thyroid cancer requires prompt treatment.
Causes of Thyroid Disease
Several factors can cause thyroid disease:
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease cause the immune system to attack the thyroid gland.
- Iodine Deficiency: Iodine is essential for hormone production; a deficiency can lead to hypothyroidism and goiter.
- Genetics: A family history of thyroid disease increases the risk.
- Medications: Drugs such as lithium and amiodarone can interfere with thyroid function.
- Radiation Therapy: Exposure to radiation, especially in the neck area, can damage the thyroid gland.
- Surgery: Removing part or all of the thyroid can lead to hypothyroidism.
Symptoms of Thyroid Disease

Symptoms vary depending on whether the condition is hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
- Hypothyroidism Symptoms:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Weight gain
- Dry skin and hair
- Cold intolerance
- Depression and memory problems
- Constipation
- Hoarse voice
- Muscle and joint pain
- Hyperthyroidism Symptoms:
- Weight loss
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Nervousness and anxiety
- Tremors in hands
- Increased sweating
- Heat intolerance
- Frequent bowel movements
- Sleep disturbances
- Bulging eyes (in Graves’ disease)
How Does Thyroid Disease Affect You?
Thyroid disease impacts overall health significantly. Hormone imbalance affects various bodily functions, leading to physical and mental health issues. Untreated thyroid disease can cause complications such as heart problems, infertility, and osteoporosis.
- Metabolism: Thyroid hormones regulate metabolism. Hypothyroidism slows it down, leading to weight gain, while hyperthyroidism speeds it up, causing weight loss.
- Energy Levels: Hypothyroidism can make you feel tired and sluggish, whereas hyperthyroidism can cause restlessness and fatigue.
- Mood and Mental Health: Thyroid disease can affect your mood, causing symptoms like depression, anxiety, and irritability.
- Cardiovascular Health: Hyperthyroidism can increase heart rate and blood pressure, while hypothyroidism can cause a slow heart rate and high cholesterol levels.
- Reproductive Health: Thyroid disease can affect menstrual cycles and fertility in women, leading to irregular periods or difficulty conceiving.
Treatment Options for Thyroid Disease
Managing thyroid disease involves proper diagnosis and treatment. Common options include:
- Medication:
- Hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone levothyroxine to normalize levels.
- Hyperthyroidism can be managed with antithyroid medications like methimazole and propylthiouracil to reduce hormone production.
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy: This treatment for hyperthyroidism involves taking radioactive iodine orally, which destroys overactive thyroid cells.
- Surgery: Surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy) may be necessary in cases of thyroid cancer or large goiters.
- Lifestyle Changes: A healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management support thyroid health. Foods rich in iodine, selenium, and zinc are beneficial.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular blood tests to monitor hormone levels ensure that treatment is effective and medication dosages are adjusted as needed.
Conclusion Thyroid disease is manageable with the right diagnosis and treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take proactive steps to manage your thyroid health. If you experience symptoms of thyroid disease, consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment. With appropriate care, you can lead a healthy and balanced life despite thyroid disease.
If you have any queries related to medical health, consult Subhash Goyal or his team members on this given no +91 88008 25789, +91 99150 99575, +918283060000