What is diabetes? This is a common question, especially for those who are affected by this condition. Diabetes, also known as high blood sugar, is a condition where the glucose levels in the blood become elevated. This happens when the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Type 2 diabetes is the most common type, often linked to lifestyle and dietary habits.
Types of Diabetes

Diabetes is mainly classified into two types – Type 1 and Type 2. In Type 1 diabetes, the body cannot produce insulin because the immune system attacks the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This type is usually diagnosed during childhood or adolescence. On the other hand, in Type 2 diabetes, the body’s sensitivity to insulin is reduced, leading to difficulty in managing blood sugar levels. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form, primarily found in adults, and is largely influenced by lifestyle factors such as diet, physical activity, and body weight.
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
There are several factors that can cause Type 2 diabetes, including:
1. Unhealthy Diet:

Consuming too much sugar and junk food leads to weight gain and causes spikes in blood sugar levels, which may eventually cause insulin resistance. Processed foods and sugary drinks are especially harmful as they contain empty calories and very little nutrition, leading to an increased risk of Type 2 diabetes. A lack of balanced nutrients affects the body’s ability to manage glucose properly.
2. Lack of Physical Activity:
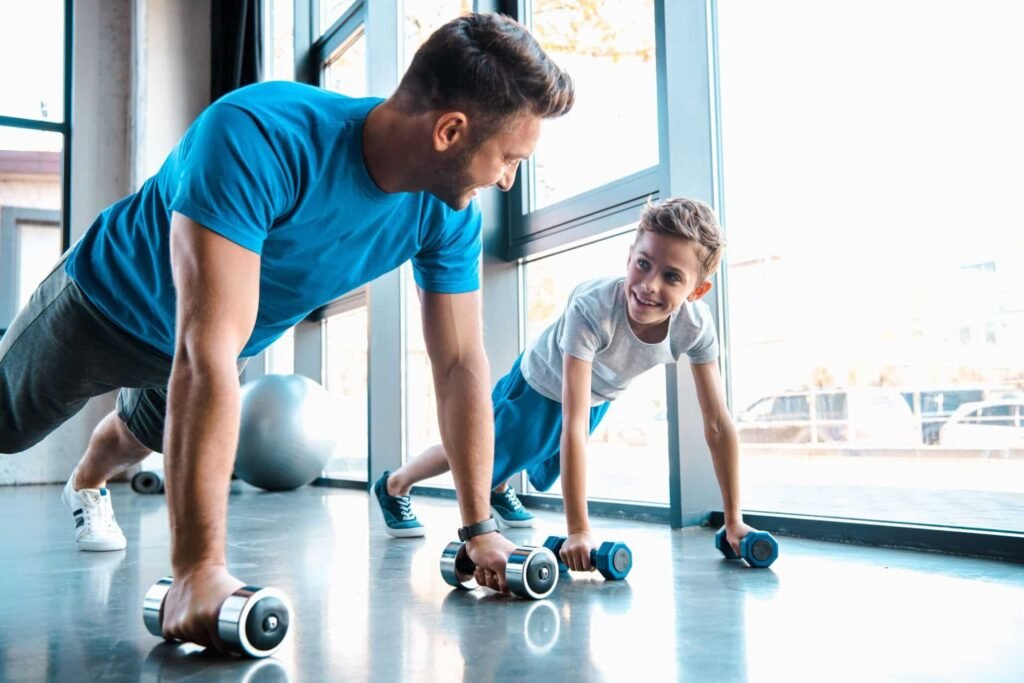

Not engaging in regular exercise can lead to obesity, which is a major risk factor for Type 2 diabetes. Physical inactivity also affects the efficiency of insulin, making it difficult for the body to use glucose for energy. Regular physical activity helps muscles absorb glucose more effectively, reducing the overall burden on the pancreas and improving insulin sensitivity. Sedentary behavior, on the other hand, is directly associated with a higher risk of developing diabetes.

3. Genetics:
A family history of diabetes increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes, especially if both parents have it. Specific genetic markers can make individuals more susceptible to insulin resistance and impaired glucose tolerance. Even though genetic factors play a role, lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk. Understanding family medical history can help in taking early preventive measures to avoid developing diabetes.
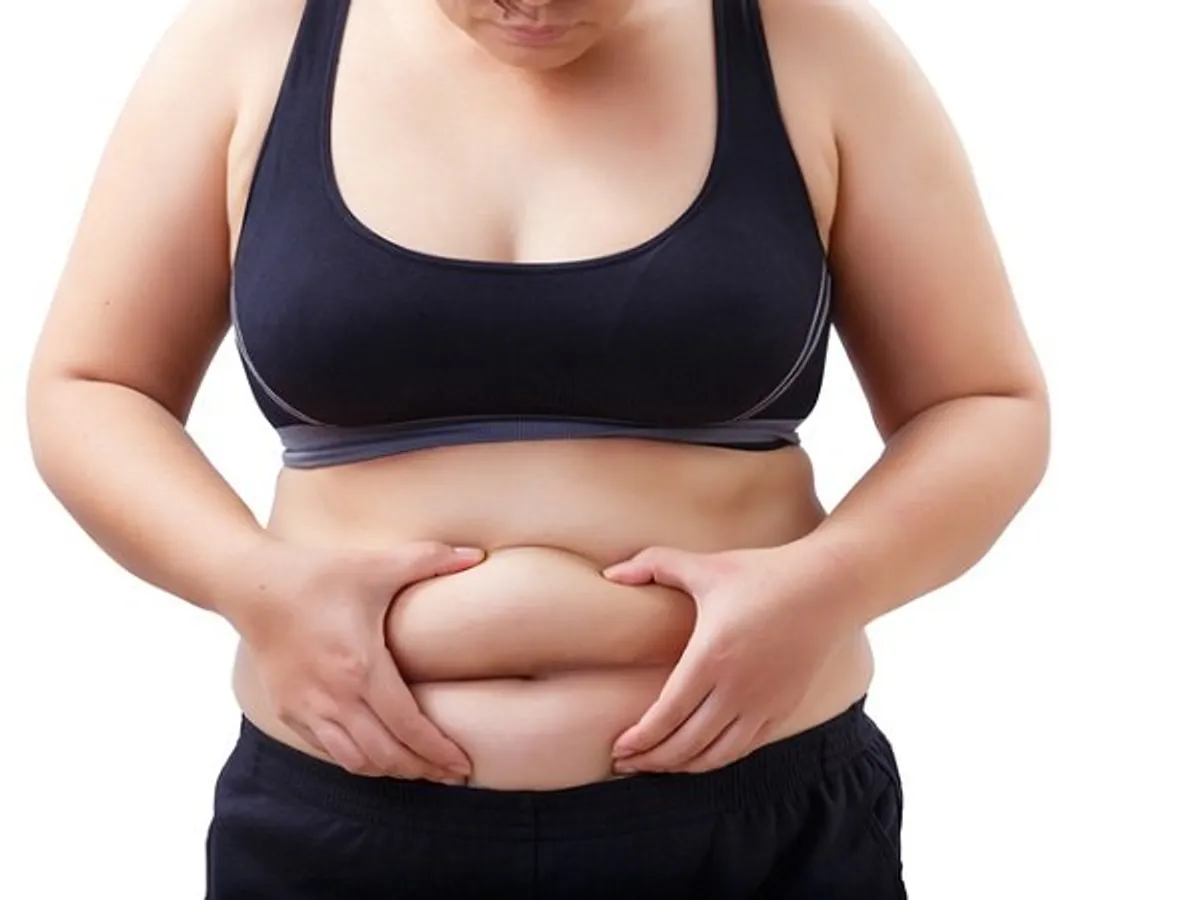
4. Obesity:
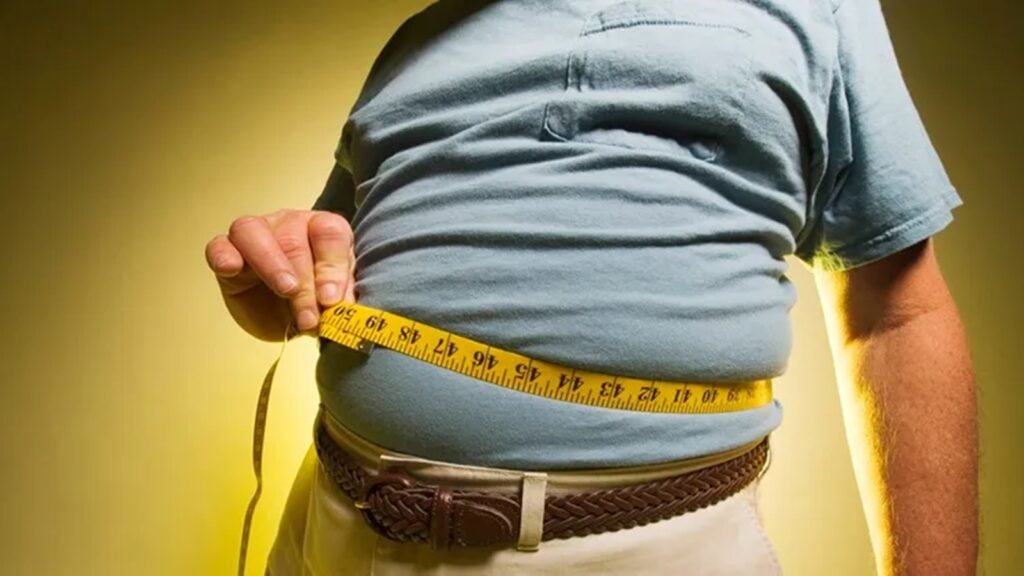

Particularly fat accumulation around the abdomen, known as visceral fat, is a strong indicator of increased risk for Type 2 diabetes. This type of fat affects hormone regulation and insulin sensitivity, which can result in elevated blood sugar levels. Abdominal fat releases certain inflammatory substances that may also interfere with the insulin process, leading to metabolic issues. Maintaining a balanced diet and staying active are crucial to preventing the accumulation of visceral fat.
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
1. Excessive Thirst:
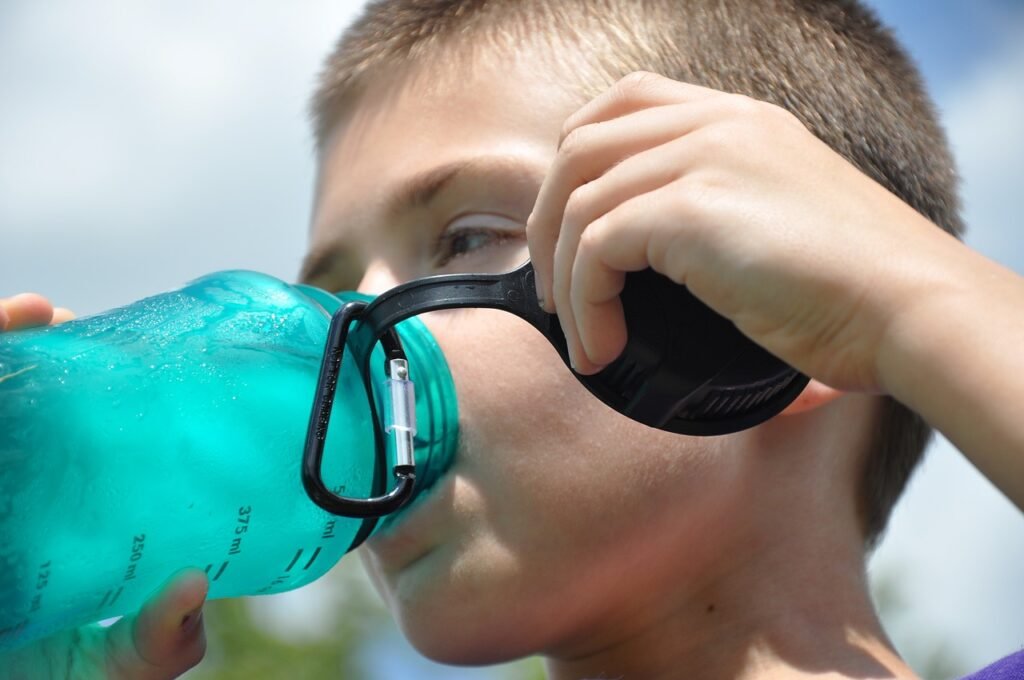

Increased thirst is a classic symptom of Type 2 diabetes. High blood sugar levels cause the body to draw water from tissues, leading to dehydration and increased thirst. It is the body’s natural mechanism to dilute the concentration of glucose in the bloodstream. Drinking plenty of water is important to prevent dehydration, but if thirst persists, it’s important to seek medical advice to check for diabetes.
2. Frequent Urination:
When blood sugar levels are elevated, the kidneys work overtime to filter and absorb the excess sugar. If the kidneys can’t keep up, the excess glucose is excreted through urine, leading to frequent urination, especially at night. This frequent need to urinate, called polyuria, is often accompanied by increased thirst and can lead to dehydration if not managed properly.
3. Fatigue and Weakness:
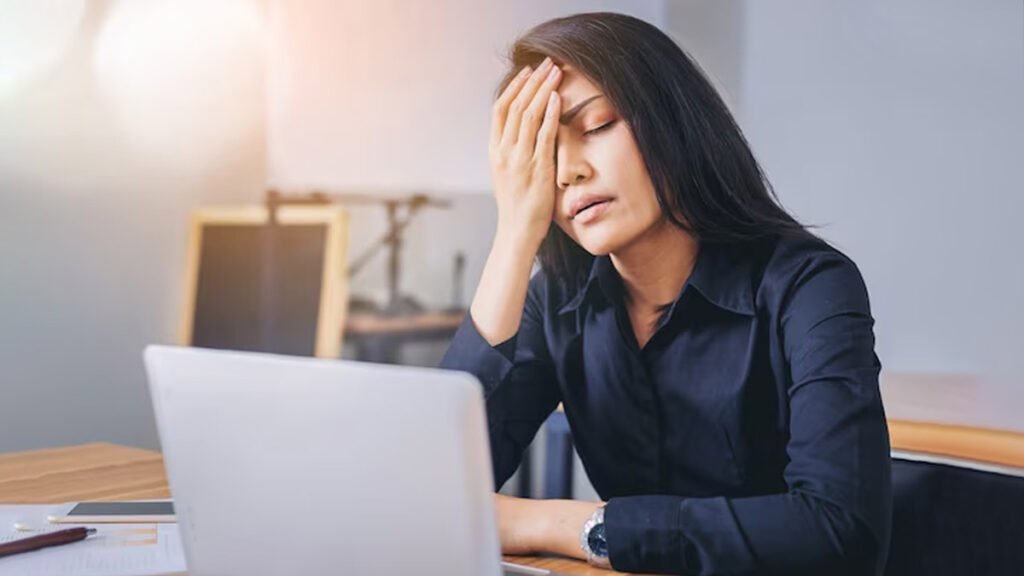

Fatigue is a common symptom of Type 2 diabetes, as the body’s cells do not receive the glucose they need for energy. Insulin resistance means that glucose remains in the bloodstream instead of entering cells, resulting in a lack of energy. This constant feeling of tiredness can affect daily activities and overall quality of life, requiring proper management of blood sugar levels.
4. Unexplained Weight Loss:
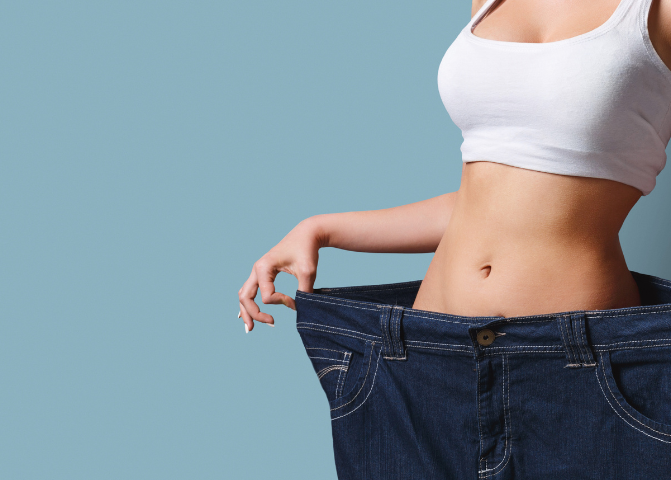

Sudden and unexplained weight loss may occur despite eating properly, as the body is unable to use glucose for energy and starts breaking down fat and muscle. This symptom is more common in untreated or poorly managed diabetes. The weight loss can lead to muscle weakness and overall physical frailty, making it important to seek early intervention to restore proper metabolic function.
Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes can be managed through a healthy lifestyle and medications. Here are some treatment options:
- Healthy Diet: Include whole grains, fruits, green vegetables, and protein-rich foods in your diet. Avoid sugar, refined carbohydrates, and fried foods that can cause spikes in blood sugar. Eating fiber-rich foods helps slow down glucose absorption and keeps blood sugar levels stable. Portion control is also key to preventing overeating, which can contribute to weight gain and insulin resistance.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in at least 30 minutes of physical activity daily, such as walking, running, or cycling. Regular exercise helps increase insulin sensitivity, meaning that cells are better able to use glucose for energy. Strength training exercises also help in building muscle mass, which further improves glucose metabolism.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight helps control blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of complications related to diabetes. Weight loss, even a modest amount, can have a significant impact on insulin sensitivity and overall glucose control. Setting realistic weight loss goals and making gradual changes in diet and activity levels can be more sustainable.
Ayurvedic Remedies
According to Ayurveda, diabetes can be treated using natural methods. Here are some home remedies:
1. Fenugreek Seeds:
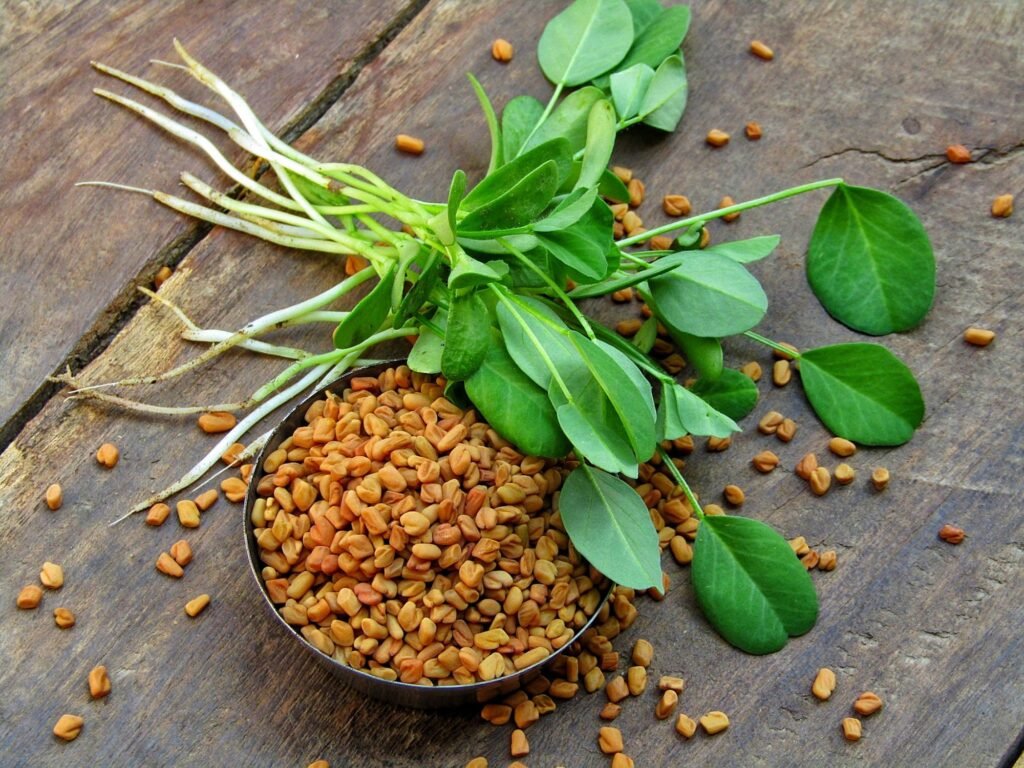

Soak fenugreek seeds overnight and consume them in the morning to help regulate blood sugar. Fenugreek contains soluble fiber that slows down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, thus improving glucose tolerance. It also enhances the body’s natural insulin production, making it a simple yet effective home remedy.
2. Bitter Gourd Juice:
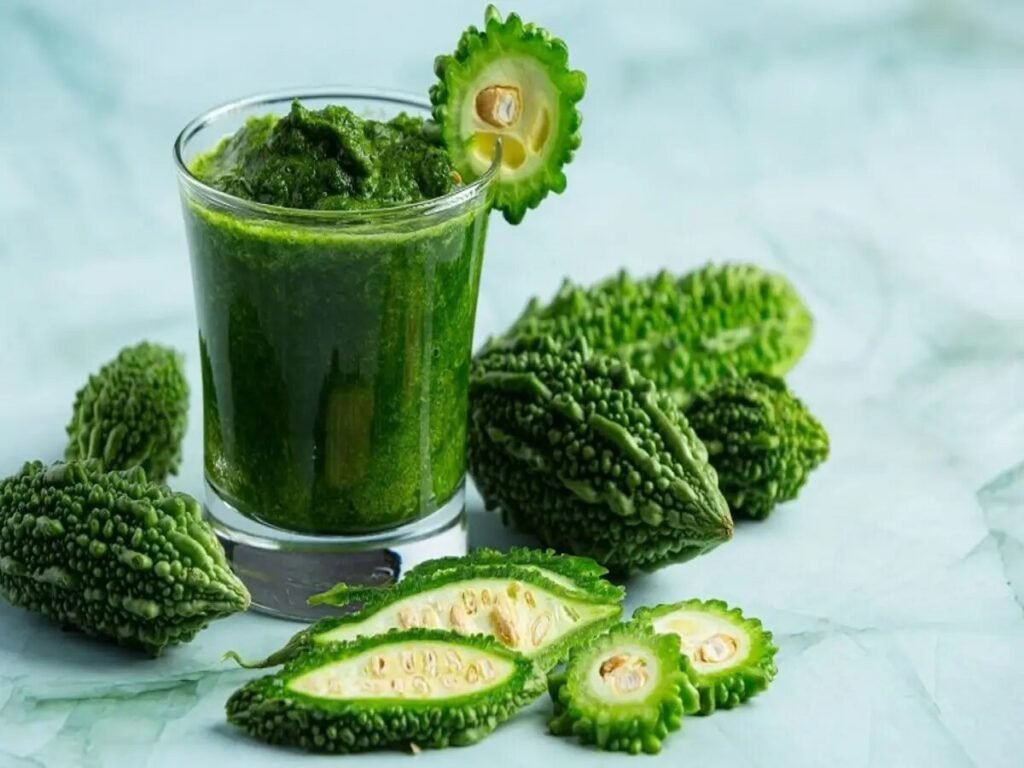

Drinking bitter gourd juice may help lower blood glucose levels as it contains compounds that have insulin-like properties. Bitter gourd, also known as karela, is rich in polypeptide-p, which helps reduce glucose levels in the blood. Consuming bitter gourd juice on an empty stomach is recommended for better results.
3. Jamun (Indian Blackberry):
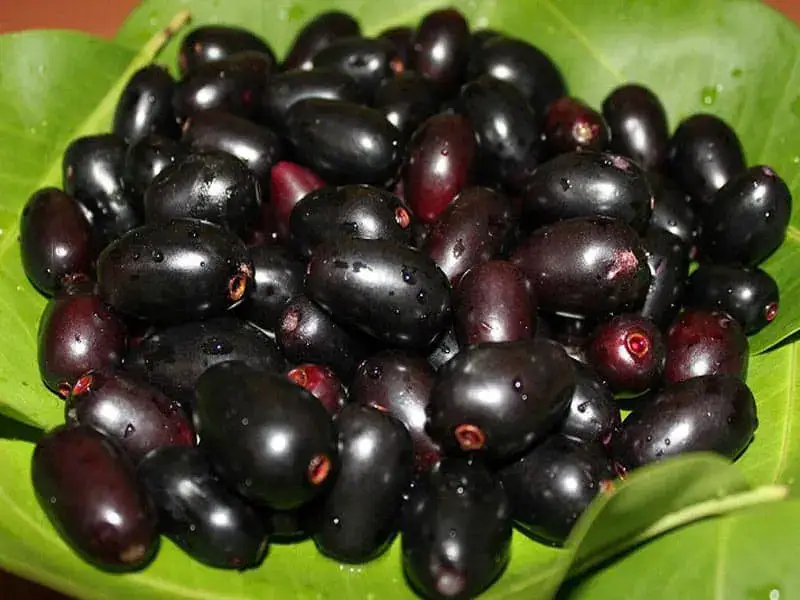

The powdered seeds of jamun are also beneficial in managing diabetes as they contain compounds that improve insulin sensitivity. Jamun helps reduce the symptoms of diabetes such as frequent urination and thirst.
Conclusion
Understanding what diabetes is crucial for recognizing and managing it in a timely manner. Type 2 diabetes can be effectively managed by adopting a healthy lifestyle, staying active, and undergoing regular medical check-ups. Pay special attention to your diet, exercise regularly, and take prescribed medications to control blood sugar levels effectively.
If you have any queries related to medical health, consult Subhash Goyal or his team members on this given no +91 88008 25789, +91 99150 99575, +918283060000