Knee pain can be a debilitating condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Whether it’s caused by injury, aging, or underlying medical conditions, understanding and managing knee pain is crucial for maintaining a healthy, active lifestyle. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the causes, symptoms, treatment options, prevention strategies, and exercises for knee pain relief.
Causes of Knee Pain

Knee pain is a prevalent issue that can be caused by a wide range of factors. Understanding the underlying causes is essential for proper diagnosis and effective treatment. Here are some common causes of knee pain:
1. Injuries

- Ligament Tears : Traumatic injuries to the knee, such as tearing the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) or medial collateral ligament (MCL), can result from sudden impacts or twisting motions. These injuries often lead to acute knee pain, swelling, and instability. Athletes involved in sports like soccer, basketball, and football are particularly prone to ligament tears.
- Meniscus Tears: The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage that acts as a cushion and stabilizer in the knee joint. Tears in the meniscus can occur due to sudden twisting movements or gradual wear and tear over time. Meniscus tears can cause sharp, localized pain, swelling, and a sensation of the knee locking.
- Fractures: Traumatic accidents or falls can lead to fractures in the bones around the knee, such as the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), or patella (kneecap). Fractures cause severe pain, swelling, and limited mobility.
2. Overuse

- Tendinitis: Repetitive activities or overuse of the knee joint can irritate the tendons that connect muscles to bones. This irritation can result in tendinitis, characterized by localized pain and swelling around the knee.
- Bursitis: The knee contains small fluid-filled sacs called bursae that act as cushions between tendons, ligaments, and bones. Overuse or excessive pressure on these bursae can lead to bursitis, causing pain, swelling, and tenderness.
3. Arthritis
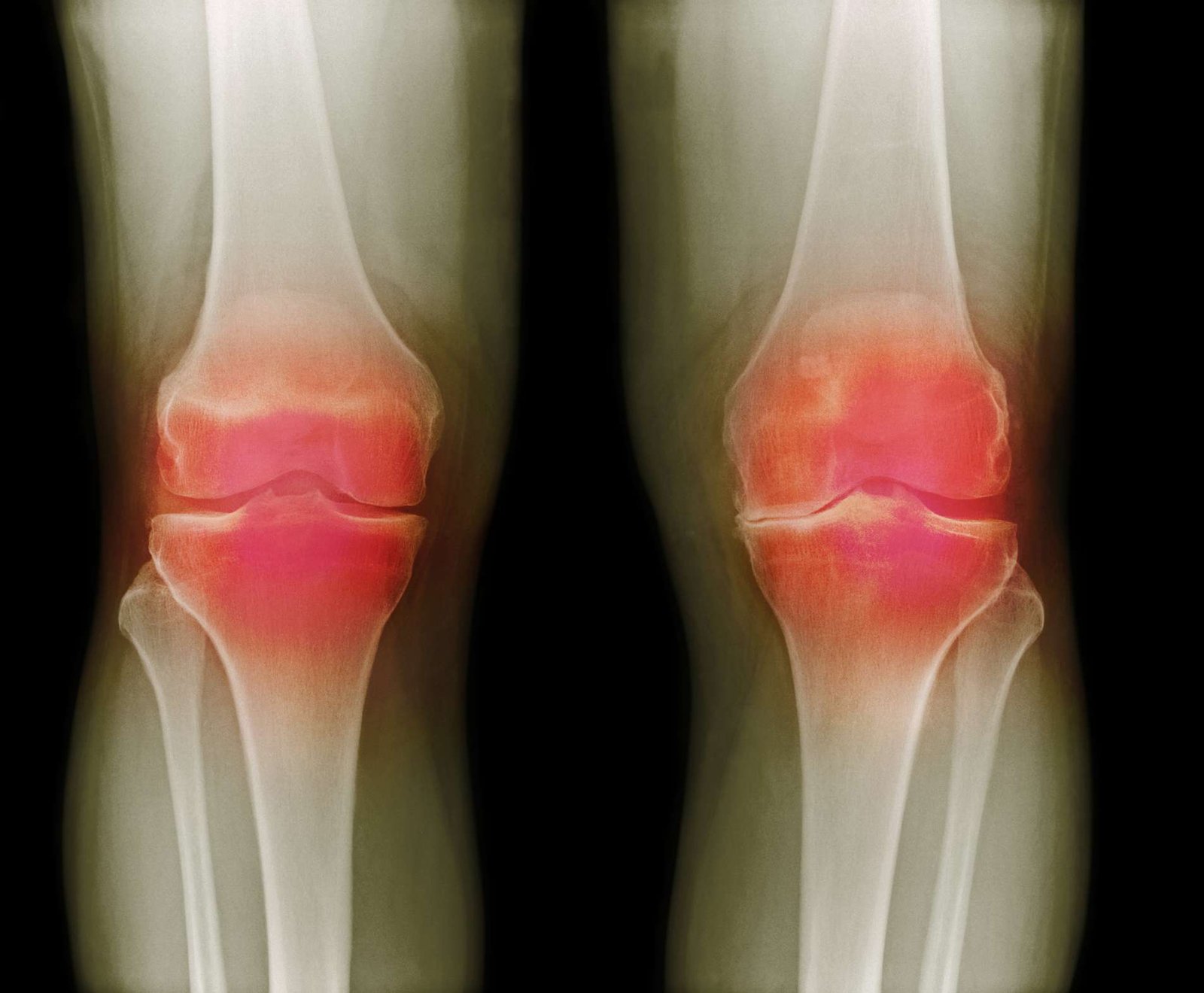
- Osteoarthritis: Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis and typically occurs as people age. It involves the gradual breakdown of the cartilage in the knee joint, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Osteoarthritis can also result from previous injuries or overuse.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition that affects the synovium (the lining of the joint). It can cause chronic inflammation in the knee joint, leading to pain, swelling, and joint damage.
- Other Forms of Arthritis: Less common forms of arthritis, such as gout or psoriatic arthritis, can also affect the knee joint and cause pain and inflammation.
Common Symptoms of Knee Pain
Recognizing the symptoms of knee pain is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Look out for the following signs:
- Pain: Dull, aching, or sharp pain in and around the knee joint.
- Swelling: Inflammation and swelling can make the knee appear larger than usual.
- Stiffness: Difficulty bending or straightening the knee.
- Clicking or popping: Audible noises when moving the knee.
- Instability: Feeling as if the knee might give way.
Treatment Options for Knee Pain
The appropriate treatment for knee pain depends on its cause, severity, and the individual’s unique circumstances. Here are some common and effective treatment approaches for managing knee pain:
1. Physical Therapy

- Physical therapy is a cornerstone of knee pain management. Skilled physical therapists can design tailored exercise programs to address specific knee issues. These exercises aim to:
- Strengthen Muscles: Targeted strengthening exercises for the muscles around the knee, including the quadriceps and hamstrings, can improve joint stability and reduce pain.
- Improve Flexibility: Stretching exercises help maintain or improve the knee’s range of motion, which can alleviate stiffness and discomfort.
- Enhance Balance and Coordination: Balance exercises can reduce the risk of falls and further injuries, especially in older individuals.
Physical therapy also includes manual techniques such as joint mobilization and soft tissue manipulation to improve joint function and reduce pain.
2. Medications
- Medications may be used to manage knee pain, depending on its underlying cause:
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter NSAIDs like ibuprofen or prescription NSAIDs can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation associated with conditions like osteoarthritis and tendinitis.
- Pain Medications: In cases of severe or chronic pain, your doctor may prescribe stronger pain medications, including opioids. However, opioids are typically reserved for situations where other treatments have not been effective due to their potential for addiction and side effects.
- Corticosteroid Injections: For conditions involving significant inflammation, such as rheumatoid arthritis or bursitis, corticosteroid injections into the knee joint can provide rapid relief. These injections have anti-inflammatory properties.
3. Knee Braces

- Knee braces provide external support and stability to the injured or painful knee. There are different types of knee braces available, including:
- Prophylactic Braces: These are often worn by athletes to prevent knee injuries, especially in contact sports.
- Functional Braces: Designed for individuals who have already experienced a knee injury, these braces provide support and protect the knee during physical activities.
- Unloader or Offloader Braces: These are used to alleviate pressure on a specific part of the knee joint, often prescribed for individuals with osteoarthritis.
- Rehabilitative Braces: These braces are typically used after knee surgery to restrict certain movements during the initial recovery phase.
If you have any queries related to medical health, consult Subhash Goyal or his team members on this given no +91 99150 72372, +91 99150 99575, +918283060000