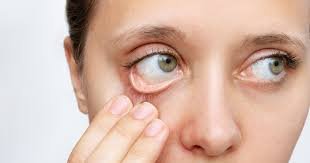
Pyorrhea, also known as periodontitis or gum disease, is a prevalent oral health condition characterized by inflammation and infection of the tissues surrounding the teeth. Understanding its types, causes, symptoms, and home remedies is crucial for effective prevention and management.
1.Types of Pyorrhea

Pyorrhea presents in various forms, with chronic periodontitis being the most common. This type progresses gradually, often over many years, and is characterized by inflammation of the gums and eventual loss of the supporting bone structure. On the other hand, aggressive periodontitis is less common but more severe. It can develop rapidly, leading to rapid bone destruction and tooth loss, particularly in young adults. Recognizing the differences between these types is crucial for determining appropriate treatment strategies and managing the condition effectively.
2.Causes of Pyorrhea
Poor oral hygiene habits, such as inadequate brushing and flossing, play a significant role in the development of pyorrhea. When plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—accumulates on the teeth and gums, it can harden into tartar, triggering inflammation and infection. Smoking is another major risk factor for pyorrhea, as it weakens the immune system and reduces blood flow to the gums, impairing their ability to fight off infection. Additionally, genetic predisposition can increase susceptibility to gum disease, while hormonal changes during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause may exacerbate symptoms.
3.Symptoms of Pyorrhea
Early signs of pyorrhea may include swollen, red, or tender gums that bleed easily, particularly during brushing or flossing. Persistent bad breath, known as halitosis, is also common due to the presence of bacteria in the mouth. As the condition progresses, gums may recede, exposing the roots of the teeth and causing sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods and beverages. Loose teeth or changes in the alignment of the bite may occur as the supporting bone deteriorates, and pockets may form between the teeth and gums, trapping food particles and bacteria.
4.Home Remedies for Pyorrhea
1.Maintain Excellent Oral Hygiene
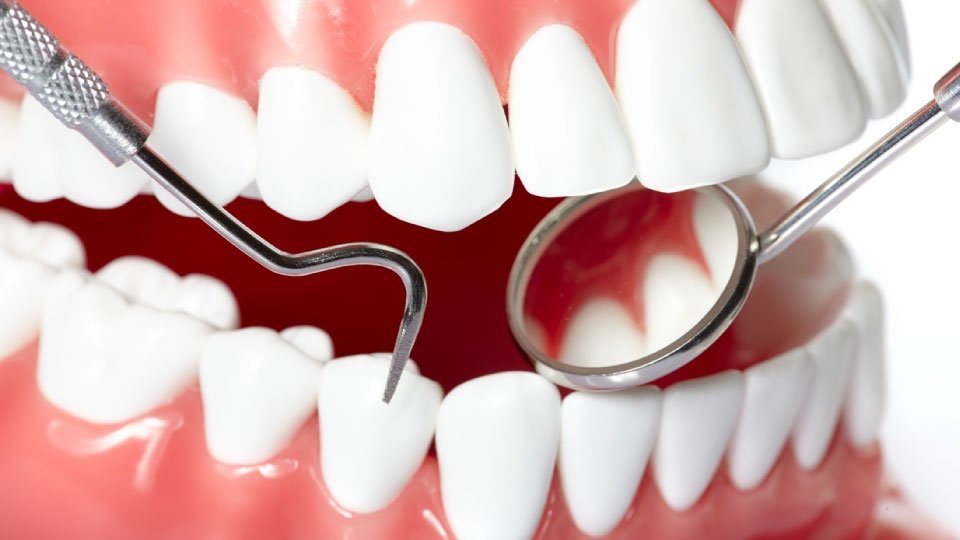
Brushing teeth at least twice a day and flossing daily are essential for removing plaque and preventing gum disease. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste to gently clean all tooth surfaces and along the gumline. Consider using an antimicrobial mouthwash or oral irrigator to further reduce bacterial buildup.
2.Rinse with Saltwater Solution

A saltwater rinse can help reduce inflammation and promote healing of the gums. Dissolve half a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and swish it around your mouth for 30 seconds to a minute before spitting it out. Repeat this several times a day, especially after meals or when experiencing discomfort.
3.Try Oil Pulling

Oil pulling involves swishing a tablespoon of coconut oil around in your mouth for 15–20 minutes, then spitting it out. This ancient practice is believed to draw out toxins and bacteria from the gums, helping to improve oral health. Perform oil pulling first thing in the morning on an empty stomach for best results.
4.Use Herbal Mouthwashes
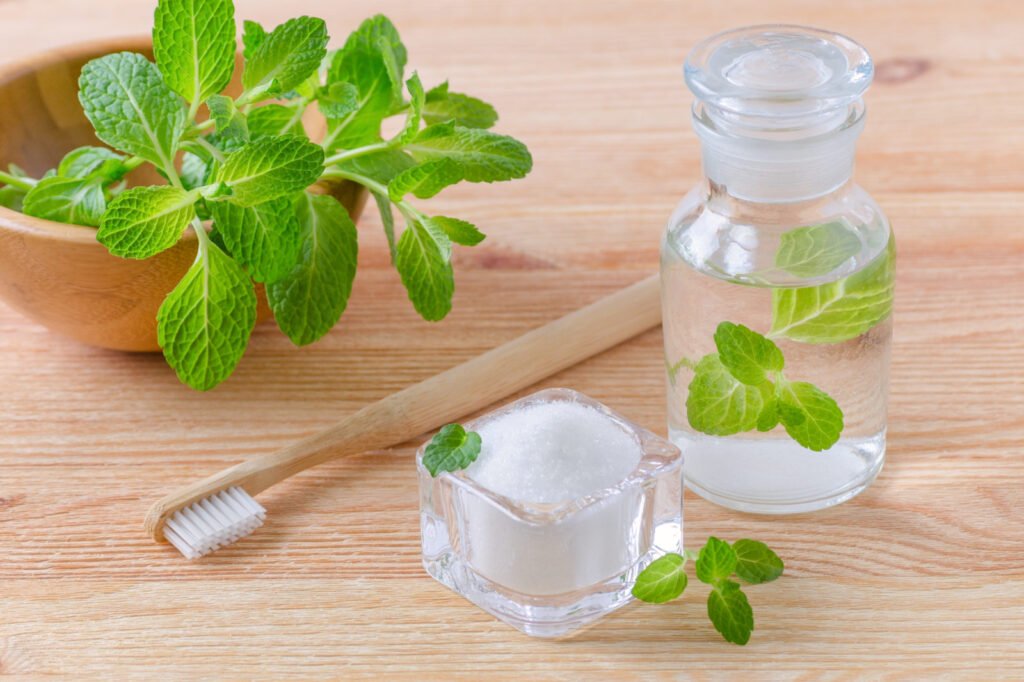

Herbal mouthwashes containing ingredients like tea tree oil, peppermint, or sage can have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties that help combat gum disease and freshen breath. Look for products specifically formulated for gum health, and use them as directed for maximum effectiveness.
5.Consume a Balanced Diet
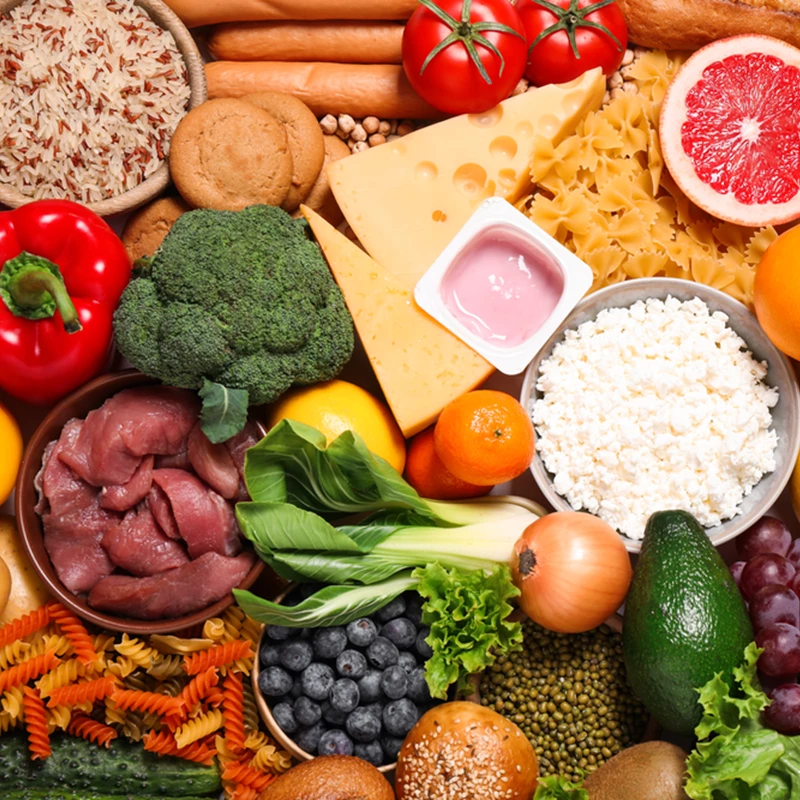

A nutritious diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants is essential for supporting overall oral health and reducing inflammation. Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains into your meals, and limit sugary snacks and beverages, which can contribute to plaque buildup and cavities.
6.Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol
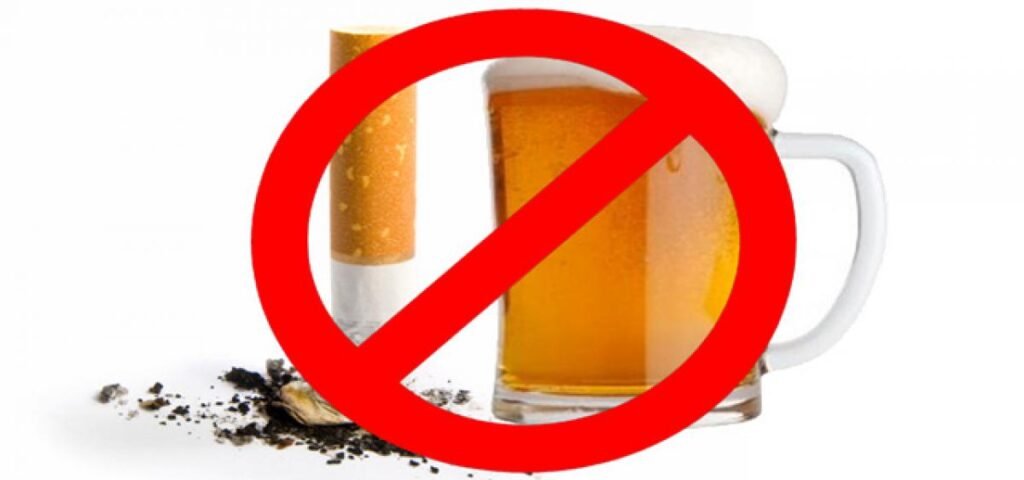

Smoking not only stains teeth and contributes to bad breath but also weakens the immune system and impairs gum health. Quitting smoking or avoiding tobacco products altogether can significantly reduce the risk of gum disease and improve overall oral health. Similarly, limit alcohol consumption, as excessive drinking can dry out the mouth and promote bacterial growth, increasing the likelihood of gum infections.
Conclusion Pyorrhea is a prevalent yet preventable oral health condition that requires proactive management and lifestyle modifications. By understanding its types, causes, symptoms, and implementing effective home remedies, individuals can take control of their oral health and reduce the risk of gum disease progression. However, it’s crucial to seek professional dental care for comprehensive treatment and regular check-ups to maintain optimal oral hygiene and prevent complications associated with pyorrhea.
If you have any queries related to medical health, consult Subhash Goyal or his team members on this given no +91 99150 72372, +91 99150 99575, +918283060000