Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects millions of people around the world. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for about 90% of all cases. Diabetes management is essential to keep blood sugar levels under control and avoid complications associated with this disease. In this article

we will discuss 10 tips for managing diabetes, including diet, exercise, and lifestyle
1. Follow a Healthy Diet

One of the most crucial steps in managing diabetes is following a healthy diet. A healthy diet can help control blood sugar levels and prevent complications associated with diabetes. People with diabetes should eat a balanced diet that includes carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats. Foods that are high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help regulate blood sugar levels.
2. Monitor Carbohydrate Intake

Carbohydrates have a significant impact on blood sugar levels, and people with diabetes need to monitor their carbohydrate intake. Carbohydrates are found in foods like bread, pasta, rice, and fruits. People with diabetes should limit their carbohydrate intake to manage blood sugar levels.
3. Eat Regular Meals

Eating regular meals is essential for people with diabetes. Skipping meals or going too long without eating can cause blood sugar levels to drop or spike. People with diabetes should eat three balanced meals a day and have snacks if needed.
4. Exercise Regularly

Exercise is essential for diabetes management. Regular exercise can help control blood sugar levels and improve overall health. People with diabetes should aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per day, such as walking, swimming, or cycling.
5. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
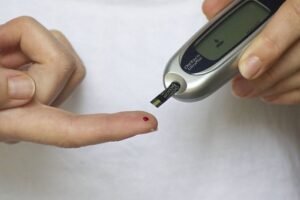
Monitoring blood sugar levels is an essential part of diabetes management. People with diabetes should check their blood sugar levels regularly and adjust their diet and medication as needed. Keeping a record of blood sugar levels can help people with diabetes track their progress and identify patterns.
6. Take Medication as Prescribed
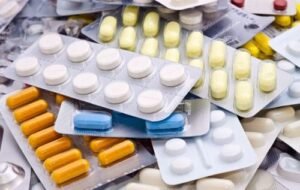
Many people with type 2 diabetes need medication to control their blood sugar levels. It’s essential to take medication as prescribed by a doctor and to follow the recommended dosage. Missing doses or taking too much medication can cause blood sugar levels to fluctuate.
7. Quit Smoking

Smoking is harmful to overall health and can increase the risk of complications associated with diabetes. People with diabetes should quit smoking to improve their health and reduce the risk of complications.
8. Manage Stress

Stress can cause blood sugar levels to rise, making diabetes management more challenging. People with diabetes should find ways to manage stress, such as practicing mindfulness meditation or deep breathing exercises.
9. Get Enough Sleep

Getting enough sleep is essential for diabetes management. Lack of sleep can cause blood sugar levels to rise, making it more challenging to manage diabetes. People with diabetes should aim for at least seven to eight hours of sleep per night.
10. Attend Regular Doctor Appointments
Regular doctor appointments are essential for diabetes management. Doctors can monitor blood sugar levels, adjust medication dosages, and provide guidance on lifestyle changes. People with diabetes should attend regular doctor appointments and follow their doctor’s recommendations.
How to control diabetes with diet and exercise?
Controlling diabetes with diet and exercise is a crucial aspect of managing this chronic disease. By making lifestyle changes, people with diabetes can improve their blood sugar control, reduce the risk of complications, and improve their overall health. Here are some tips on how to control diabetes with diet and exercise:
1.Follow a Balanced Diet:

Eating a healthy, balanced diet is essential for diabetes management. A balanced diet includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats. Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and high-fat foods. People with diabetes should also limit their carbohydrate intake and choose complex carbohydrates instead of simple carbohydrates.
2. Monitor Portion Sizes:
Controlling portion sizes is crucial for managing diabetes. Eating too much food, even if it’s healthy, can cause blood sugar levels to spike. Use measuring cups and spoons to ensure that you’re eating the right amount of food.
3. Exercise Regularly:

Regular exercise is essential for diabetes management. Exercise helps improve blood sugar control, reduce the risk of complications, and improve overall health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, at least five days a week.
4. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels:
Monitoring blood sugar levels is an essential part of diabetes management. People with diabetes should check their blood sugar levels regularly and adjust their diet and exercise as needed. Keeping a record of blood sugar levels can help people with diabetes track their progress and identify patterns.
5. Stay Hydrated:

Drinking enough water is essential for diabetes management. Drinking water can help regulate blood sugar levels and prevent dehydration. Avoid sugary drinks, such as soda and juice, which can cause blood sugar levels to spike.
6. Choose Healthy Snacks:
Snacking can be a part of a healthy diet, but it’s essential to choose healthy snacks. Opt for snacks that are low in sugar, such as nuts, seeds, and vegetables. Avoid processed snacks, such as chips and cookies.
7. Get Enough Sleep:

Getting enough sleep is crucial for diabetes management. Lack of sleep can cause blood sugar levels to rise, making it more challenging to manage diabetes. Aim for at least seven to eight hours of sleep per night.
8. Reduce Stress:

Stress can cause blood sugar levels to rise, making diabetes management more challenging. People with diabetes should find ways to manage stress, such as practicing mindfulness meditation or deep breathing exercises.
9. Take Medication as Prescribed:
Many people with type 2 diabetes need medication to control their blood sugar levels. It’s essential to take medication as prescribed by a doctor and to follow the recommended dosage. Missing doses or taking too much medication can cause blood sugar levels to fluctuate.
How can diabetes be managed by changing lifestyle?
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. While medication is often necessary to manage diabetes, making lifestyle changes can also play a significant role in diabetes management. Here are some ways that diabetes can be managed by changing lifestyle:
-
Healthy Eating:
A healthy diet is essential for diabetes management. People with diabetes should focus on eating foods that are low in sugar and carbohydrates and high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats. They should also limit their intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and high-fat foods.
-
Weight Management:
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for diabetes management. Excess body weight can make it more challenging to regulate blood sugar levels and increase the risk of complications. People with diabetes should aim to maintain a healthy weight through a combination of healthy eating and regular exercise.
-
Quit Smoking:
Smoking is harmful to overall health and can also make diabetes management more challenging. People with diabetes should quit smoking to reduce the risk of complications and improve their overall health.
-
Regular Check-ups:
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential for diabetes management. Healthcare providers can monitor blood sugar levels, adjust medication as needed, and provide guidance on lifestyle changes.
In conclusion, managing diabetes by changing lifestyle involves adopting healthy habits, such as healthy eating, regular exercise, weight management, blood sugar monitoring, quitting smoking, stress management, and regular check-ups with a healthcare provider. By making these changes, people with diabetes can improve their blood sugar control, reduce the risk of complications, and improve their overall health.