Diabetes, a condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, has become a global health concern, affecting millions of people worldwide. At its core, the cause of diabetes involves a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors that impair the body’s ability to regulate glucose. This condition is broadly categorized into Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, each stemming from different causes yet leading to the same challenge: managing blood sugar levels. Type 1 diabetes is primarily an autoimmune condition, where the body mistakenly attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. In contrast, Type 2 diabetes is often the result of insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s cells fail to respond efficiently to insulin, coupled with progressive pancreatic beta-cell failure.
What is the Main Cause of Diabetes?

Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. The main cause of diabetes varies depending on the type. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, while Type 2 diabetes is primarily caused by insulin resistance and lifestyle factors such as obesity, lack of physical activity, and poor diet. Understanding the cause of diabetes is essential for effective management and prevention strategies.
What are the 4 Stages of Diabetes?
1.Insulin Resistance

At this initial stage, the body’s cells start to resist insulin’s effects, making it challenging for insulin to escort glucose from the bloodstream into cells. This resistance leads to an accumulation of glucose in the blood, prompting the pancreas to produce more insulin in an attempt to overcome this resistance and normalize blood sugar levels. Lifestyle factors such as obesity, lack of physical activity, and a diet high in processed foods can significantly contribute to insulin resistance.
2.Prediabetes

During the prediabetes stage, blood sugar levels are elevated beyond normal thresholds but are not yet high enough for a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. This stage serves as a critical warning sign, indicating that without intervention, the progression to diabetes is likely. Lifestyle modifications at this stage, including improved diet, regular exercise, and weight loss, can be highly effective in reversing prediabetes and preventing the onset of type 2 diabetes.
3.Diabetes
When blood sugar levels are consistently high, diabetes is diagnosed through various tests, including fasting blood glucose, HbA1c, and oral glucose tolerance tests. This stage is marked by the body’s inability to produce sufficient insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or use insulin effectively (Type 2 diabetes), requiring management through medication, dietary changes, and lifestyle adjustments to control blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
4.Complications Stage
Without proper management of diabetes, chronic high blood sugar levels can lead to long-term damage to organs and tissues, resulting in complications such as neuropathy (nerve damage), nephropathy (kidney damage), retinopathy (eye damage), cardiovascular diseases, and increased risk of infections. Early diagnosis and effective management of blood sugar levels, along with regular monitoring and treatment of any complications, are vital to reducing the risk and severity of these long-term consequences.
How Does Diabetes Affect You?
Diabetes affects the body in numerous ways, including increased risk for heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems. It can also lead to slower wound healing and increased susceptibility to infections. Managing blood sugar levels and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are key to minimizing these risks.
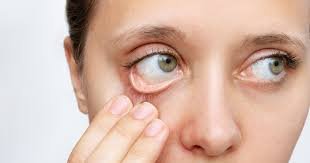
What are the 5 Warning Signs of Diabetes?
- Frequent Urination: High blood sugar levels can lead to increased urination.
- Excessive Thirst: The body’s attempt to flush out excess sugar can result in feeling thirsty.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Especially common in Type 1 diabetes.
- Fatigue: High blood sugar levels can make you feel more tired than usual.
- Blurred Vision: High glucose levels can affect your eyesight.
What is Normal Sugar Level by Age?
Blood sugar levels can vary based on age, but generally, for most adults without diabetes, fasting blood sugar levels should be between 70 to 99 mg/dL, and postprandial (after eating) levels should be less than 140 mg/dL. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for age-specific recommendations and individual health conditions.
How Can We Control Sugar?

Managing blood sugar involves a combination of diet, exercise, and sometimes medication. Eating a balanced diet rich in fiber and low in refined sugars, maintaining a regular exercise routine, monitoring blood sugar levels, and adhering to medication plans are all crucial steps. Incorporating low-glycemic fruits like strawberries can be part of a healthy diet for people with diabetes, providing essential nutrients without significantly spiking blood sugar levels.
Conclusion
People with diabetes can enjoy strawberries in moderation as part of a balanced diet. These fruits offer numerous health benefits and can contribute to blood sugar management when consumed wisely. Understanding the cause of diabetes, recognizing its stages and warning signs, and knowing how to control blood sugar are vital steps in managing diabetes effectively. With the right strategies, individuals with diabetes can lead healthy, fulfilling lives.
If you have any queries related to medical health, consult Subhash Goyal or his team members on this given no +91 99150 72372, +91 99150 99575, +918283060000