Dehydration is a common but often overlooked condition that can lead to serious health issues if not properly addressed. It’s vital to understand the intricacies of dehydration, from its root causes to its symptoms, and to equip oneself with practical knowledge on maintaining optimal hydration levels. This article delves deep into these aspects, offering insights and actionable tips to safeguard your health through proper hydration.
Causes of Dehydration

Understanding the various factors that contribute to dehydration is the first step in prevention. Beyond just not drinking enough water, several other conditions can lead to fluid loss:
- Insufficient Water Intake: The most straightforward cause is simply not consuming enough water daily. The human body requires a significant amount of water to function correctly, and without adequate intake, dehydration quickly sets in.
- Excessive Sweating: Whether from an intense workout session or just being out in the sun, sweating excessively without replenishing lost fluids can lead to dehydration. Sweat is your body’s way of cooling down, but it also means you’re losing vital water.
- Fever: When your body temperature rises, it tries to cool down by sweating, which can rapidly deplete your fluid levels. The higher the fever, the greater the risk of dehydration.
- Diarrhea and Vomiting: These conditions can cause a significant and rapid loss of fluids and electrolytes, leading to dehydration. This is especially concerning in young children and the elderly.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels lead to increased urination and fluid loss, posing a risk for dehydration. Managing diabetes and maintaining blood sugar levels can help mitigate this risk.
Each of these causes highlights the importance of being proactive about hydration, especially in situations that increase fluid loss.
Symptoms of Dehydration

The body gives off several signals when it’s running low on fluids. Recognizing these early symptoms is crucial for preventing dehydration:
- Thirst: While thirst is an obvious indicator, by the time you feel thirsty, you may already be dehydrated. It’s a sign your body is signaling for more fluids.
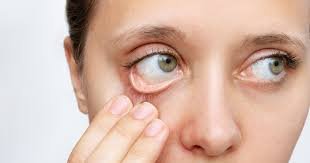
- Dry Mouth and Skin: A lack of hydration affects saliva production, leading to a dry mouth. Skin may also lose its elasticity, becoming dry and more prone to wrinkling.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Without enough water, your body can’t properly transport oxygen and nutrients to your cells, leading to feelings of weakness and tiredness.
- Headaches: Dehydration reduces your brain’s fluid levels, causing it to pull away from the skull slightly, leading to pain.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Low fluid levels decrease blood volume, lowering blood pressure and causing dizziness, especially when standing up quickly.
- Dark-Colored Urine: The kidneys conserve water when dehydrated, leading to more concentrated and darker urine. This is a clear indicator that you need to drink more fluids.
Early recognition and response to these symptoms can prevent the progression to more severe dehydration.
Tips to Stay Hydrated
Maintaining adequate hydration doesn’t have to be a chore. Here are some effective strategies to ensure you’re getting enough fluids:
- Drink Plenty of Water: Make it a habit to drink water throughout the day, not just when you’re thirsty. Setting reminders can help make this a routine.
- Eat Water-Rich Foods: Incorporate hydrating foods into your diet. Many fruits and vegetables, such as cucumbers, strawberries, and peaches, are over 90% water and can help boost your hydration.
- Monitor Your Urine Color: Keeping an eye on the color of your urine is an easy way to gauge your hydration level. Aim for a pale straw color as an indicator of proper hydration.
- Carry a Water Bottle: Having a water bottle with you at all times encourages regular water intake and makes it more convenient to hydrate.
- Limit Diuretics: Beverages that increase urination, such as coffee and alcohol, can contribute to fluid loss. Enjoy these in moderation and always counterbalance with water intake.
- Hydrate Before, During, and After Exercise: Physical activity increases sweat production, so it’s important to drink water before, during, and after exercise to compensate for lost fluids.
Adopting these hydration practices can significantly impact your overall health and well-being, ensuring that your body functions optimally and remains energized and healthy.
Conclusion
Dehydration is a preventable condition that, when ignored, can lead to more serious health complications. By understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and employing practical hydration strategies, you can protect yourself and enhance your health. Start today by making hydration a priority in your daily routine, and experience the positive changes it brings to your physical and mental well-being.
If you have any queries related to medical health, consult Subhash Goyal or his team members on this given no +91 99150 72372, +91 99150 99575, +918283060000